
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in influencing cancer risk. Several lifestyle factors contribute to the development of cancer. Here are some key lifestyle risk factors:
-
Tobacco Use: Smoking and the use of tobacco products are major contributors to various cancers, including lung, mouth, throat, pancreas, and bladder cancers.
-
Diet and Nutrition: Poor dietary habits, such as a high intake of processed foods, red and processed meats, and low consumption of fruits and vegetables, are linked to an increased risk of certain cancers.
-
Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular physical activity is associated with a higher risk of developing various types of cancer, including breast, colorectal, and endometrial cancers.
-
Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy and frequent alcohol consumption is a known risk factor for cancers of the liver, breast, esophagus, and mouth.
-
Obesity: Being overweight or obese is linked to an increased risk of several cancers, including breast, colorectal, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers.
-
UV Radiation Exposure: Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds, increases the risk of skin cancer.
-
Infections: Certain infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis B and C, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), can contribute to the development of specific cancers.
-
Environmental Factors: Prolonged exposure to environmental pollutants, carcinogens, and occupational hazards can elevate the risk of cancer.
-
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women has been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
-
Reproductive and Sexual Behavior: Certain reproductive and sexual behaviors, such as having multiple sexual partners or starting menstruation early and entering menopause late, can impact the risk of certain cancers.
It's important to note that individual cancer risk is influenced by a combination of factors, including genetics and environmental exposures. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, and protecting against UV radiation, can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer. Regular screenings and early detection also play a crucial role in cancer prevention and management.
Latest Blogs
-

-
10 Questions to Ask Your Cancer Surgeon Before Surgery
21 August, Admin
-

-
Knowing These 6 Signs of Throat Cancer Can Save Your Life
27 July, Admin
-
-
How Jaipur’s Best Cancer Surgeons Are Changing Lives
18 July, Admin
-

-
How Do I Choose A Cancer Hospital For Treatment?
08 July, Admin
-
-
Bridging Hope: How a Cancer Surgeon Changes Lives
29 June, Admin
-

-
Symptoms of Neck and Head Cancer
11 June, Admin
-

-
When Is the Best Time to Visit a Cancer Hospital in India
30 May, Admin
-

-
Understanding the Most Common Types of Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
16 May, Admin
-

-
Lifestyle Risk Factors of Cancer
19 January, By Admin
-
-
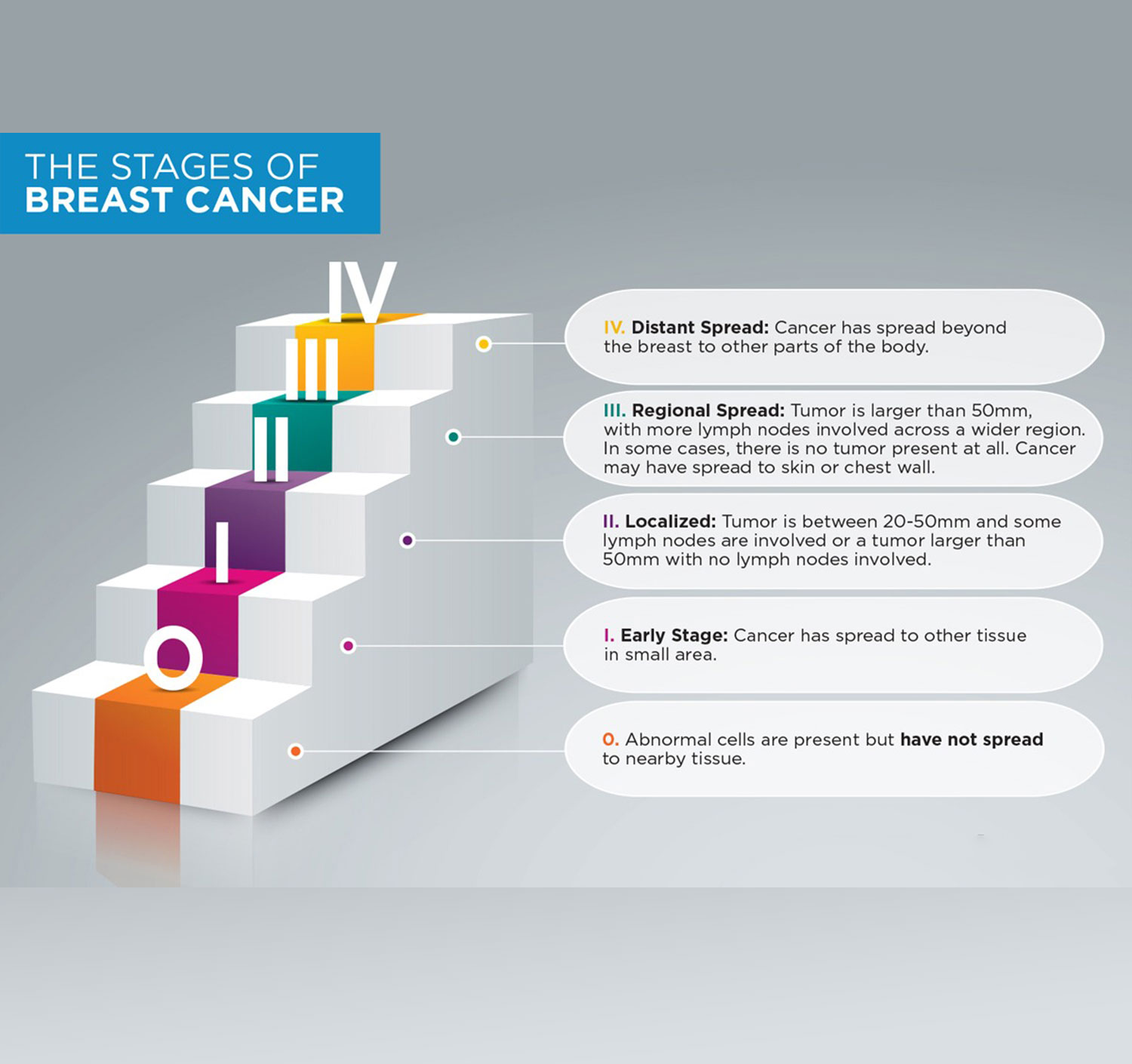
The Stages of Breast Cancer
19 January, By Admin

